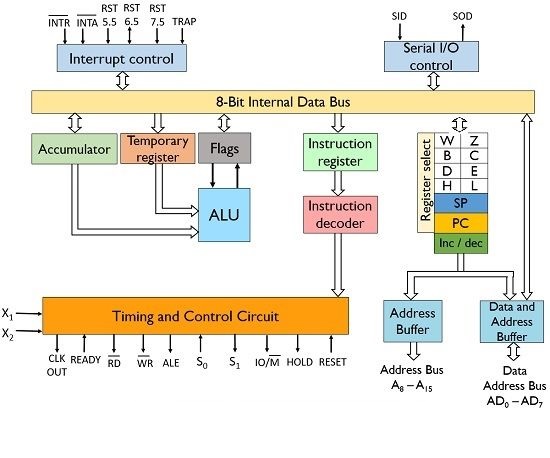
Intel 8085 is an 8-bit microprocessor with a capacity to address 216 memory locations - 64 KB. It can perform 8-bit operations at a time. It needs a single 5 V power supply with a clock running at a frequency ~3 MHz .
Architecture of 8085 Microprocessor:
General Purpose Registers are a set of registers which are located inside the 8085 microprocessor. They can store and process 8 bit data. These registers are B,C,D,E,H and L. They can be combined to form pairs BC,DE and HL in order to enable the execution of 16-bit operations.
General purpose registers are accessible to the programmer through the 8085 instruction set. They are used to insert and transfer data.
Temporary Registers :
These registers are used by the ALU to store the data on temporary basis and these are not accessed by the programmer. These are of 2 types:
- Temporary data register – It is an 8-bit register that holds the operand and provides it to the ALU for program execution. Also, the immediate results are stored by the ALU in this register.
- W and Z register – These registers are also used to hold the temporary values. It is used by the control section of the microprocessor so as to store the data during operations.
Program Counter (PC) :
It is basically a special purpose register that is used to store the address of the memory location of the instruction to be performed. It is a 16-bit register as it stores address.
It functions in such a way that it fetches the opcode from one memory location and simultaneously get incremented by the next memory location. Thus, it provides sequencing of the program to be executed.
Stack Pointer (SP) :
It is a 16-bit register and is a part of memory. The data is stored in the stack in serial format and stack pointer generally stores the address of the last data element stored in the stack. Thus the stack is based on LIFO.
Whenever a new data is added in the stack, then the stack pointer starts pointing towards the very next memory location. When a data element is removed from the stack, then the stack pointer points to previous occupied memory location.
Accumulator :
It is an 8-bit register that stores the result of the operation performed by the ALU. It is known as register A.
Flags :
Flag register basically holds the status of the current result generated by the ALU and not the actually generated result. Thus we can say it is used to test the data conditions.
8085 has 5 flags that shows 5 different data conditions. These are carry, sign, zero, parity and auxiliary carry flags.